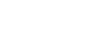Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are at the heart of modern industrial automation, enabling remote monitoring and control of various processes. With industries increasingly adopting digitalization and automation, the demand for professionals skilled in SCADA systems is on the rise. In this article, we will explore SCADA training, its importance, the different types of training available, and the career opportunities it opens up.
What is SCADA?
SCADA is a system of software and hardware elements that allows industrial organizations to control processes locally or remotely, monitor, gather, and process real-time data, and directly interact with devices such as sensors, valves, pumps, and motors through human-machine interface (HMI) software. SCADA systems are crucial in industries such as manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and transportation, where they ensure efficient, reliable, and safe operations.
Why is SCADA Training Important?
SCADA training is essential for several reasons, particularly in industries where precise control and real-time monitoring are critical. Here’s why SCADA training is vital:
Operational Efficiency: SCADA systems help improve operational efficiency by providing real-time data, enabling quick decision-making, and optimizing processes.
Enhanced Security: With cyber threats on the rise, SCADA training ensures that professionals can secure industrial control systems against potential attacks.
Industry Demand: There is a growing need for professionals who can design, implement, and manage SCADA systems across various industries.
Career Advancement: Proficiency in SCADA opens up numerous career opportunities in automation, control systems engineering, and industrial IT.
There are various SCADA training programs available, each catering to different levels of expertise. Below, we outline the most common types of training programs.
1. Basic SCADA Training
Basic SCADA training is aimed at beginners who are new to SCADA systems and industrial automation. The key areas covered include:
Introduction to SCADA: Understanding the basic components, architecture, and functions of SCADA systems.
HMI Basics: Learning how to use HMI software to monitor and control industrial processes.
Data Acquisition: Understanding how SCADA systems collect and process data from field devices.
Basic Troubleshooting: Developing skills to diagnose and resolve common issues in SCADA systems.
2. Advance SCADA Training
For those with a basic understanding of SCADA, intermediate training programs provide deeper insights into more complex aspects of SCADA systems. Topics covered include:
SCADA Programming: Learning to program SCADA systems using industry-standard software like Wonderware, Siemens WinCC, or GE Proficy.
Communication Protocols: Understanding the communication protocols used in SCADA systems, such as Modbus, DNP3, and OPC.
Integration with PLCs: Learning how SCADA systems interface with PLCs to control and monitor industrial processes.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Gaining expertise in identifying and fixing issues in SCADA systems more efficiently.
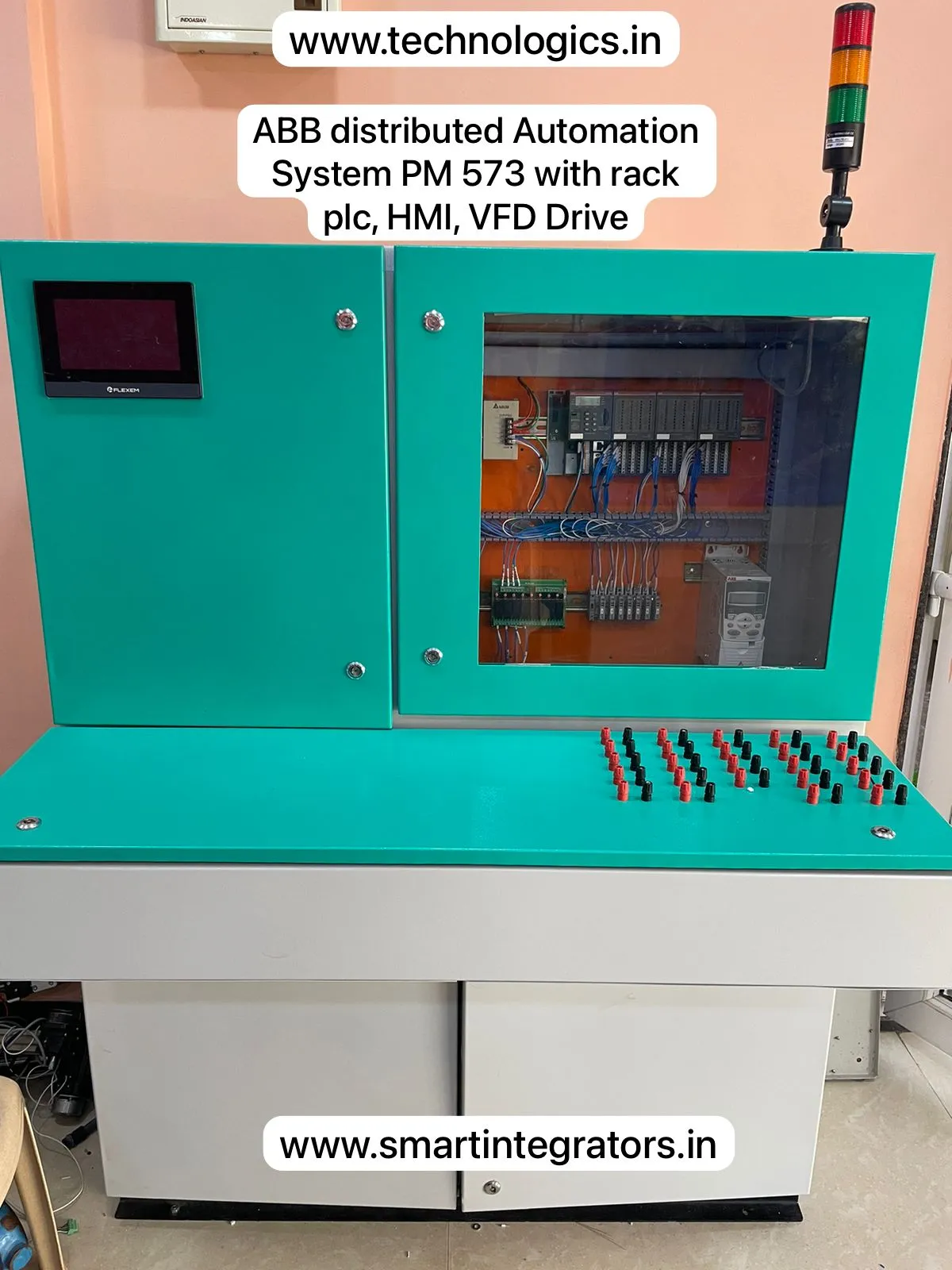
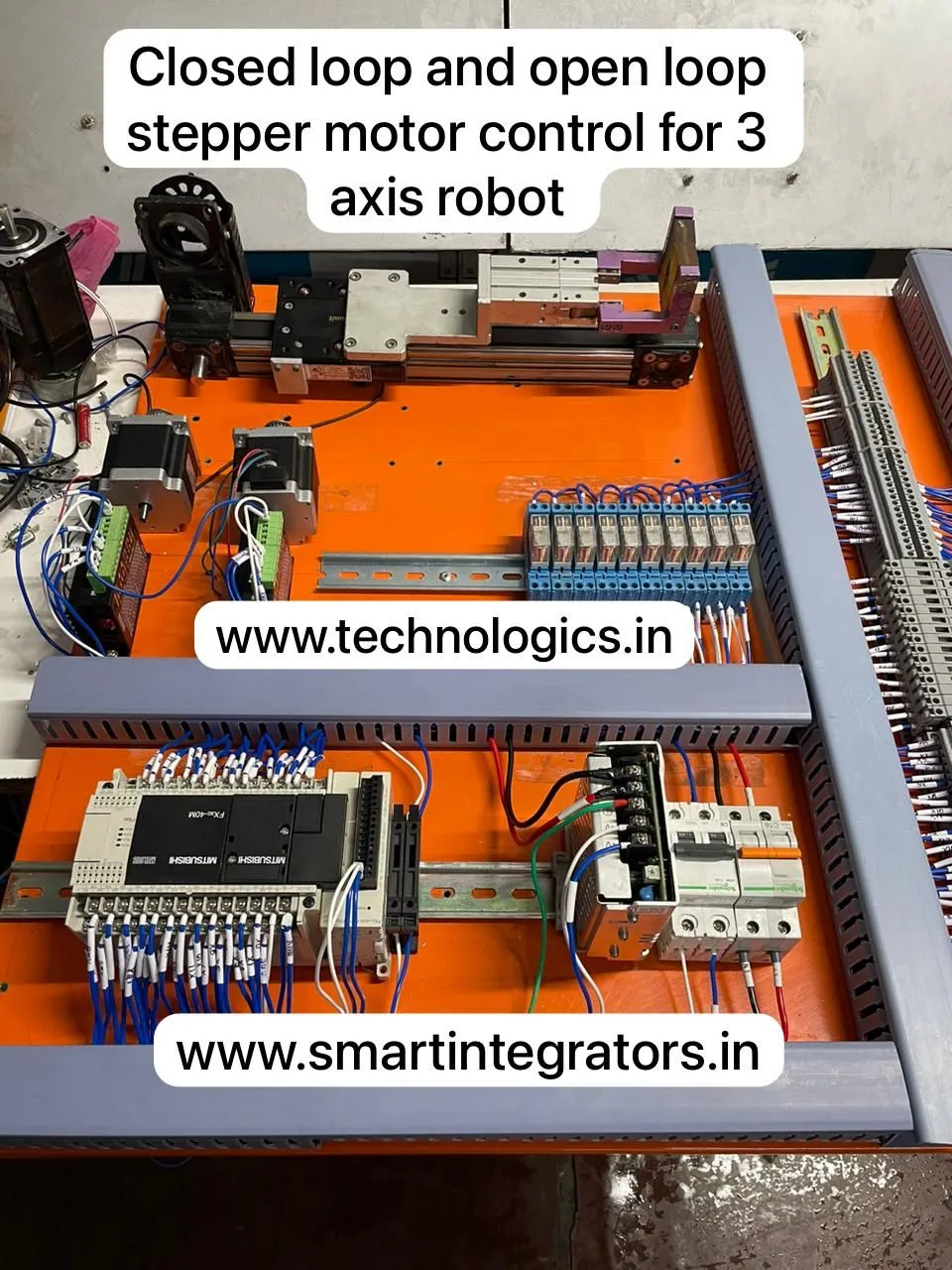
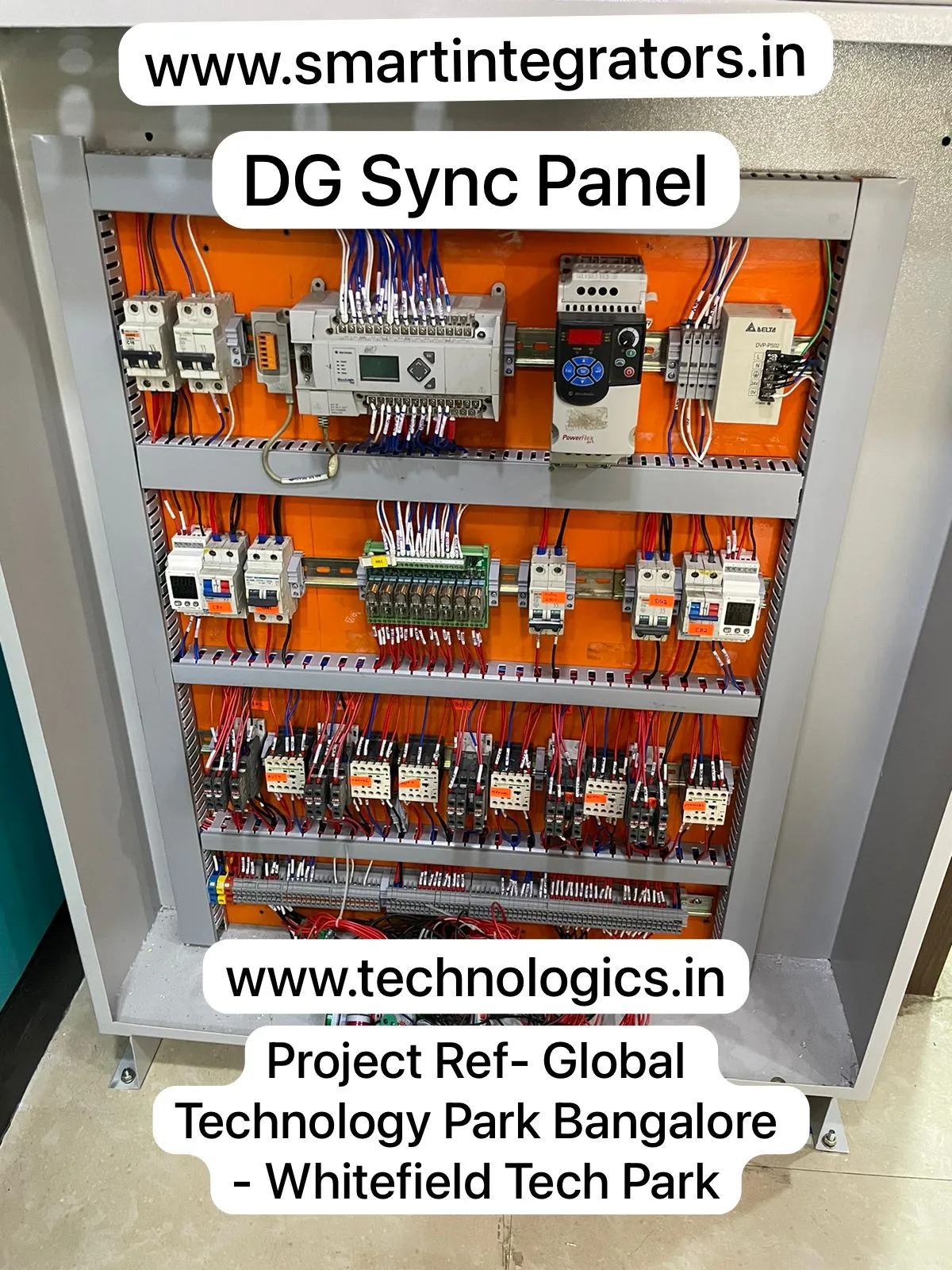
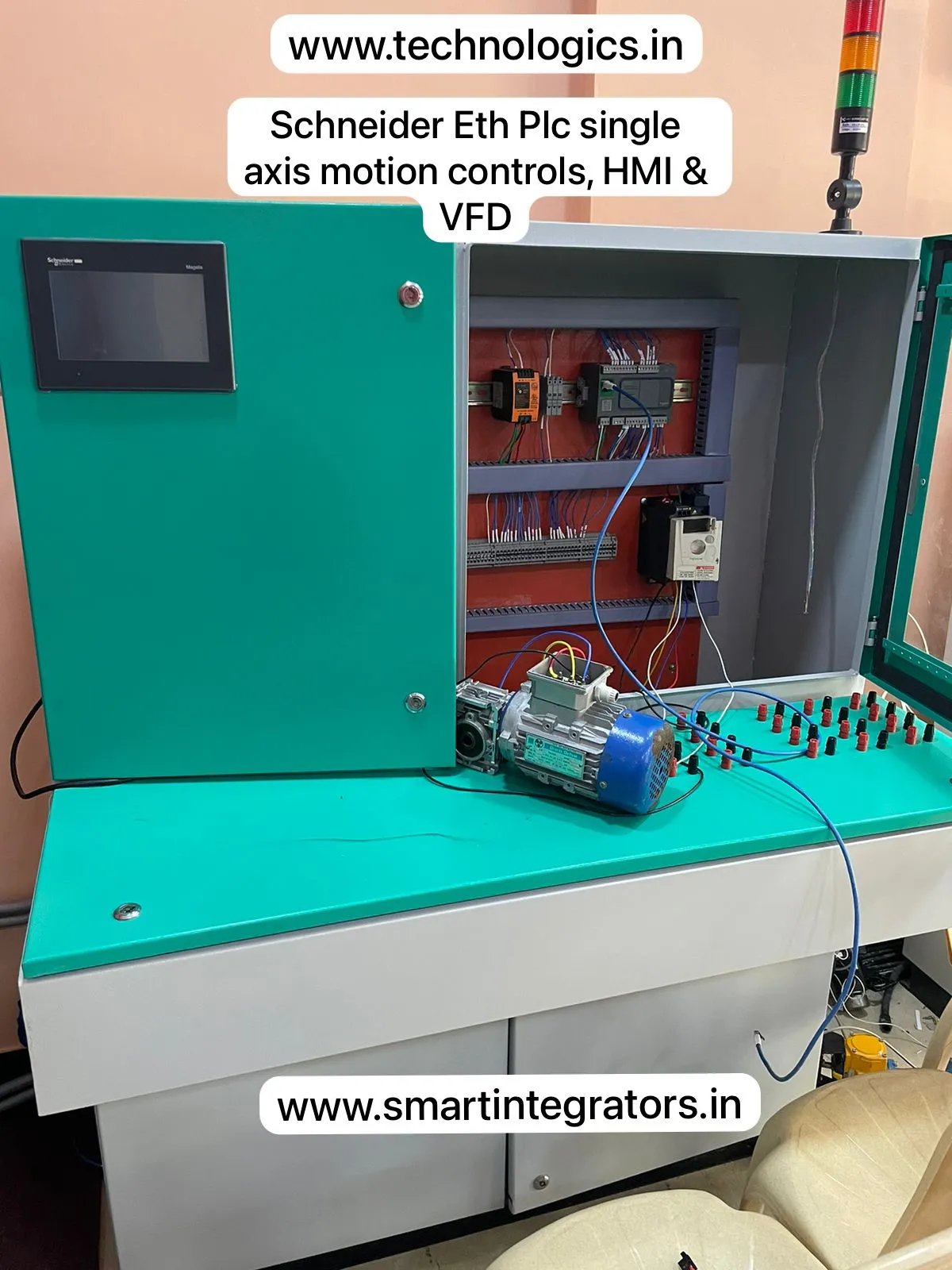
Hand’s On PLC SCADA Training in Programming, Wiring, Testing & Commissioning
- Genuine Placement
- 85k Enrolled
- All levels
- English

Training Overview
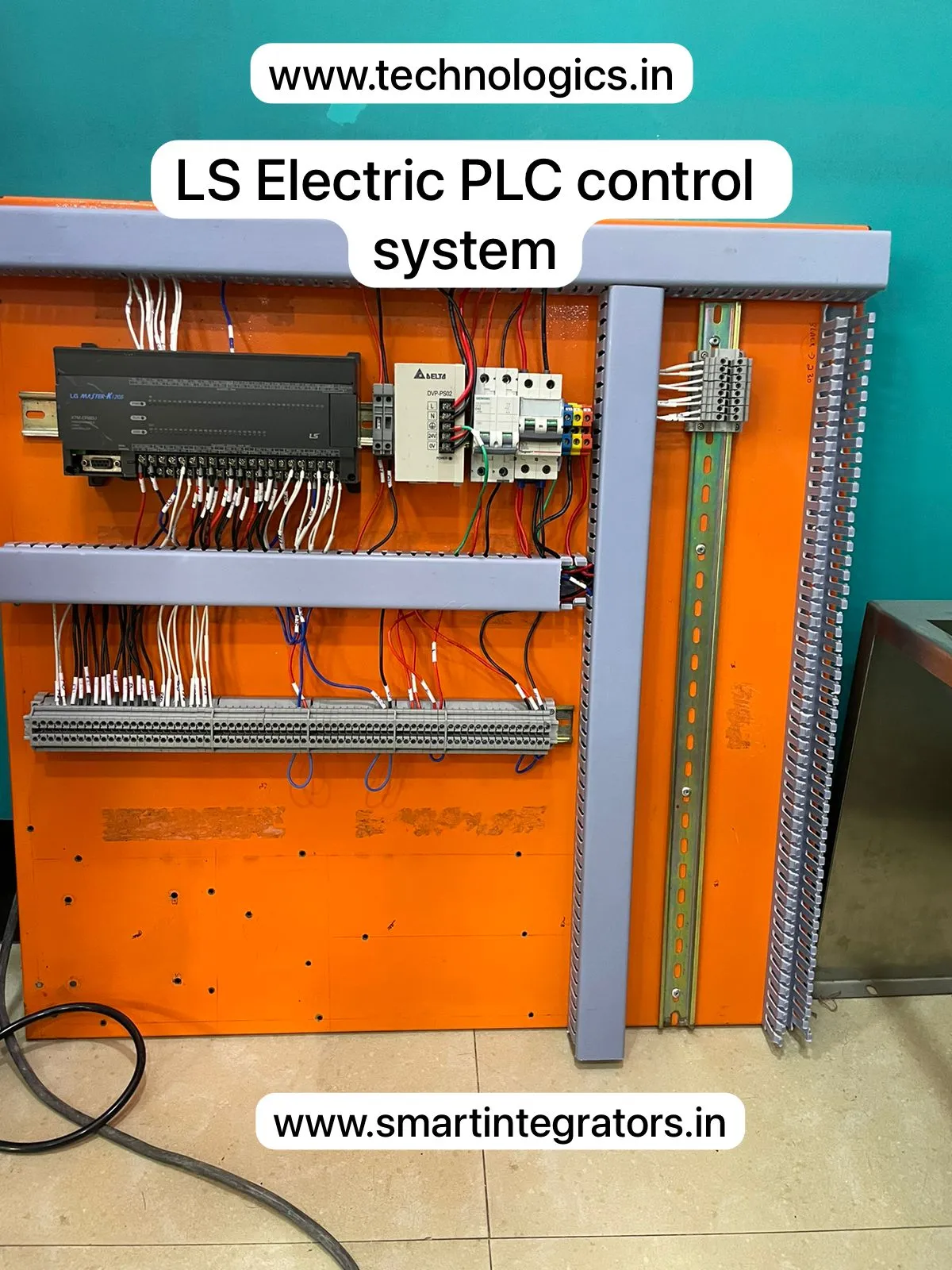
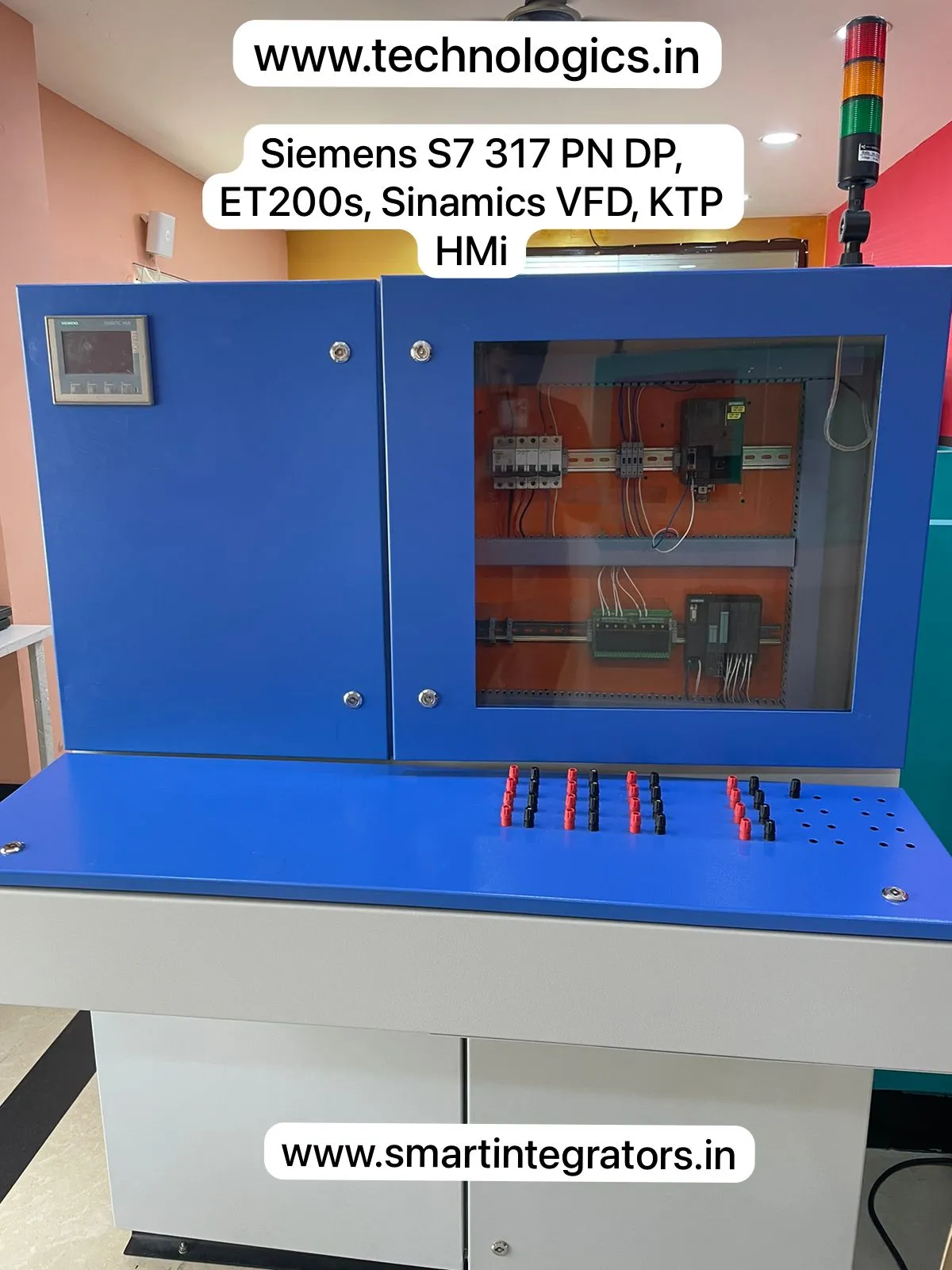
| PLC Training | ABB, Siemens, Delta, Schnieder, AB, Omron, Mitsubhishi, Keyence. |
|---|---|
| SCADA Training | Wincc, Wonderware, FactoryTalk, CCW, Kingview, Diaview. |
| HMI Training | Omron, Delta, Schnieder, AB. |
| VFD Training | ABB, Delta, Schnieder, AB. |
| DCS Training | PCS 7, ABB. |
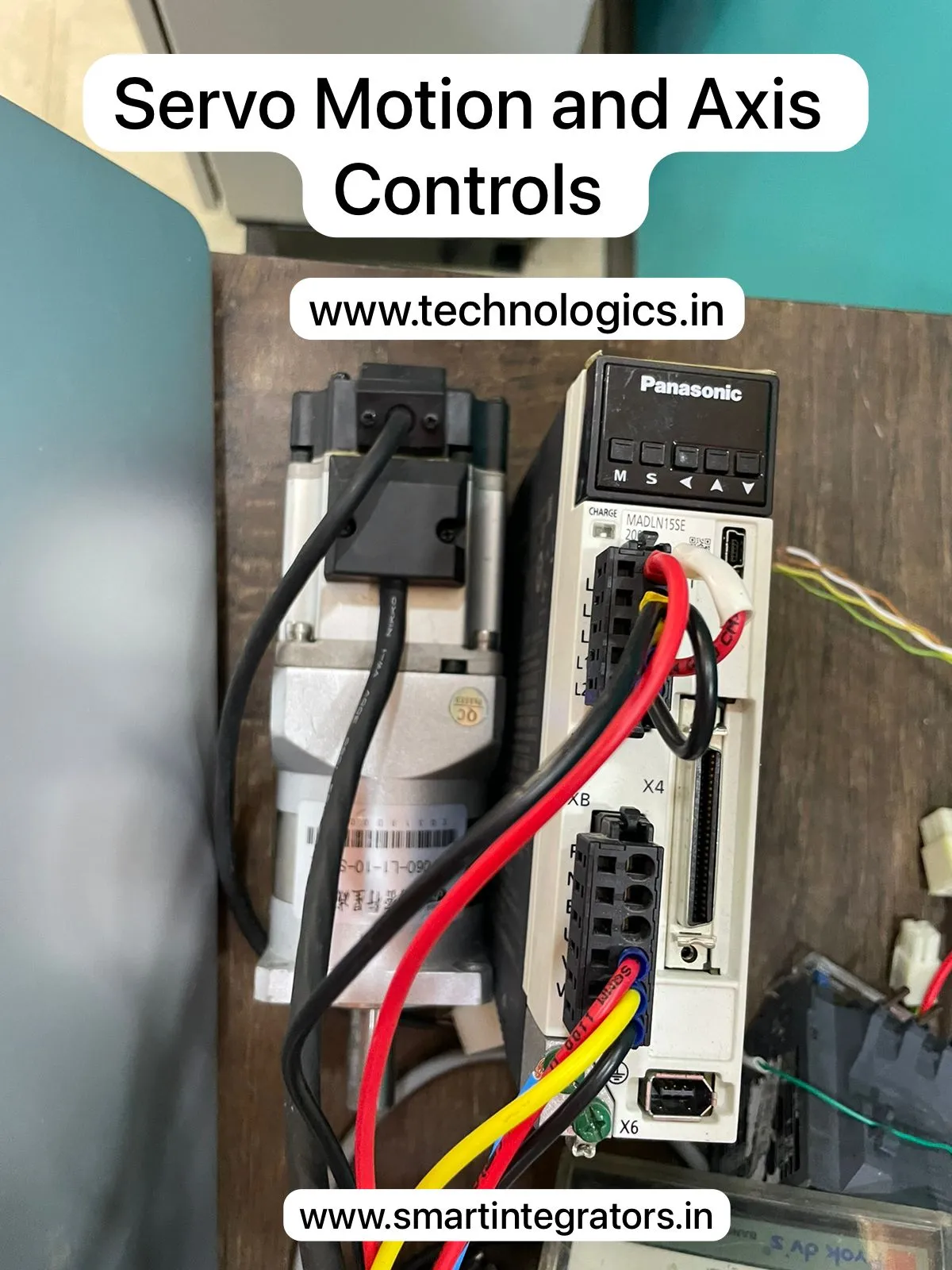
| Servo & Stepper Motor Training | Panasonic Drives, Delta. |
| Energy Meter | Schnieder, Emeasure, Trinity. |
| Relay Logics | Logic Design and Wiring |
Syllabus - In Detail
The primary and overall objective of this course is to give a hands-on experience of PLC, SCADA, VFD, HMI, DCS, Field Instruments.
- Introduction about industrial automation
- History of industrial automation, Need of automations in industries
- Example for industrial automation
- Automation control circuit and power circuit
- Field Instruments, Types and working of field devices
- Automation using relays and field devices
- Examples for relays and field devices & Logical functions done by relays and field devices
- Introduction about Programmable Logic Controller, History of PLC, Architecture of PLC
- CPU, IO Modules, Power Supply and Communications, Input and Output Devices, Need of PLC for Industrial Automation
- Types of PLC Models, Introduction about PLC Programming
- Types of Programming Languages, Introduction about PLC Programming software
- Ladder logic diagram, Structure of program, Procedure for creating ladder diagram, Logical function done by ladder program in software.
- Interfacing the field component to PLC, Sink and Source type wiring, Need of push button for industrial automation
- Importance of latching and unlatching concepts, Memory concept.
- Working with – All Major Brands of PLC
- Interlocking & Trip concept
- Types of interlocking, Need of interlocking
- Timers, Types of timers & Example Problem for automation using timers
- Need for counters & Types of counters – Example for automation using counters
- Jump and subroutine & Importance of loop instruction – Examples : Automation using Jump and Subroutine. – Upload and Download Program.
- Introduction, definition and history of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition,
- Typical SCADA System Architecture, Communication Requirements,
- SCADA systems in operation and control of interconnected power system, Power System Automation, Petroleum Refining Process, Water Purification System, Chemical Plant
- Remote Terminal Unit (RTU), RTU Configuration, RTU Hardware Modules
- Project Creation in Display, Tags, Library, Run Time, Security, Working with Properties, Animation, Alarm Setup, Trend, Language Switching, Interfacing PLC to SCADA.
- Industrial Project Documents
- P&ID Diagrams & IO List Preparation
- VFD Selection, Functions of VFD Switches & Symbols,
- Operate motor using VFD Console switches.
- Parameterisation, Checking Load, rated Voltage & current
- Comissionining, No Load Test, Speed Modulation, ON/ OFF Command, Trip Status, PID Tuning
- Interfacing PLC To VFD, Real Time Interface to PLC SCADA
- Intro to HMI
- Designining In HMI- Diffrent Types of Operaters, Textual & Graphical
- Properties for Design, I/O Configuration, Wiring of HMI, Data Handling
- Configuration & Interfacing from PLC to PC
- DCS – Distributed Control System
- Architecture of DCS, Hardware Configuration , I/O Modules, Communication Module, Troubleshooting
- I/O Wirining, Programming, CPU IP Setting & Addressing, Node Addressing, Upload & Download Monitoring,
- SCADA Interfacing, Fault Detection, Operater Interface, Designing, OPC / ODBC
- Communication Protocol, Ethernet
- Projects, Assignments & Test
Placements